Bin YanI am a research scientist at ByteDance, working in the Bay Area of California. I obtained doctorate degree at the IIAU-Lab in Dalian University of Technology, under the supervision of Prof. Huchuan Lu. During my PhD career, my main research interests are Computer Vision and Deep Learning, especially in the visual perception. Now I am dedicated in Generative AI, especially image and video generation. I spent a wonderful time at ETH Computer Vision Lab (CVL) and Google Zurich as an academic guest and a student researcher respectively from 2023 to 2024. Before that, I also worked as a research intern at Microsoft Research Asia and the ByteDance AI Lab, from 2020-2021 and 2021-2022 respectively. Before that, I completed my bachelor's degree at Dalian University of Technology, China in 2019. Email / GitHub / Google Scholar / |
|
Selected Publications |
|
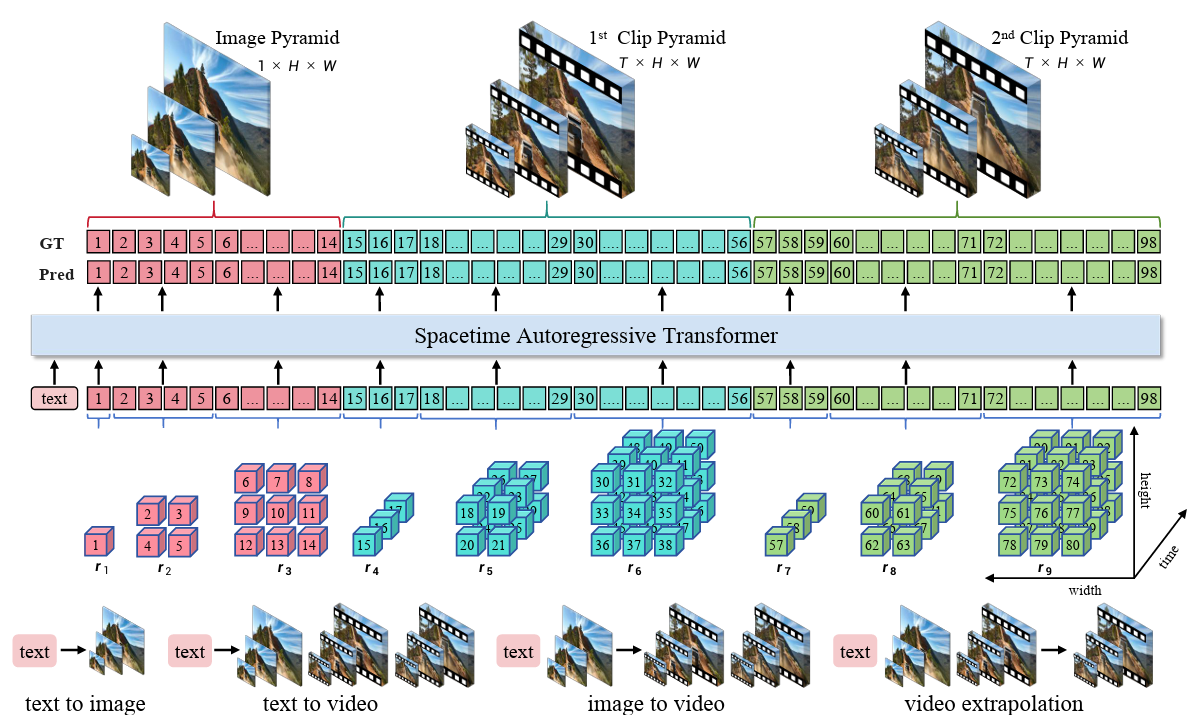
[11] InfinityStar: Unified Spacetime AutoRegressive Modeling for Visual GenerationJinlai Liu, Jian Han, Bin Yan, Hui Wu, Fengda Zhu, Xing Wang, Yi Jiang, Bingyue Peng, Zehuan Yuan NeurIPS, 2025 (Oral Presentation) arxiv / code / We present InfinityStar, a unified spacetime autoregressive framework for a variety of generation tasks such as textto-image, text-to-video, image-to-video, and long interactive video synthesis. InfinityStar outperforms all autoregressive models by large margins, even surpassing some diffusion competitors like HunyuanVideo. Without extra optimizations, our model generates a 5s, 720p video approximately 10× faster than leading diffusion-based methods. |

|
[10] Infinity ∞: Scaling Bitwise AutoRegressive Modeling for High-Resolution Image SynthesisJian Han, Jinlai Liu, Yi Jiang, Bin Yan, Yuqi Zhang, Zehuan Yuan, Bingyue Peng, Xiaobing Liu CVPR, 2025 (Oral Presentation) arxiv / code / We present Infinity, a Bitwise Visual AutoRegressive Modeling capable of generating high-resolution, photorealistic images following language instruction. Infinity redefines visual autoregressive model under a bitwise token prediction framework with an infinite-vocabulary tokenizer & classifier and bitwise self-correction mechanism, remarkably improving the generation capacity and details. |

|
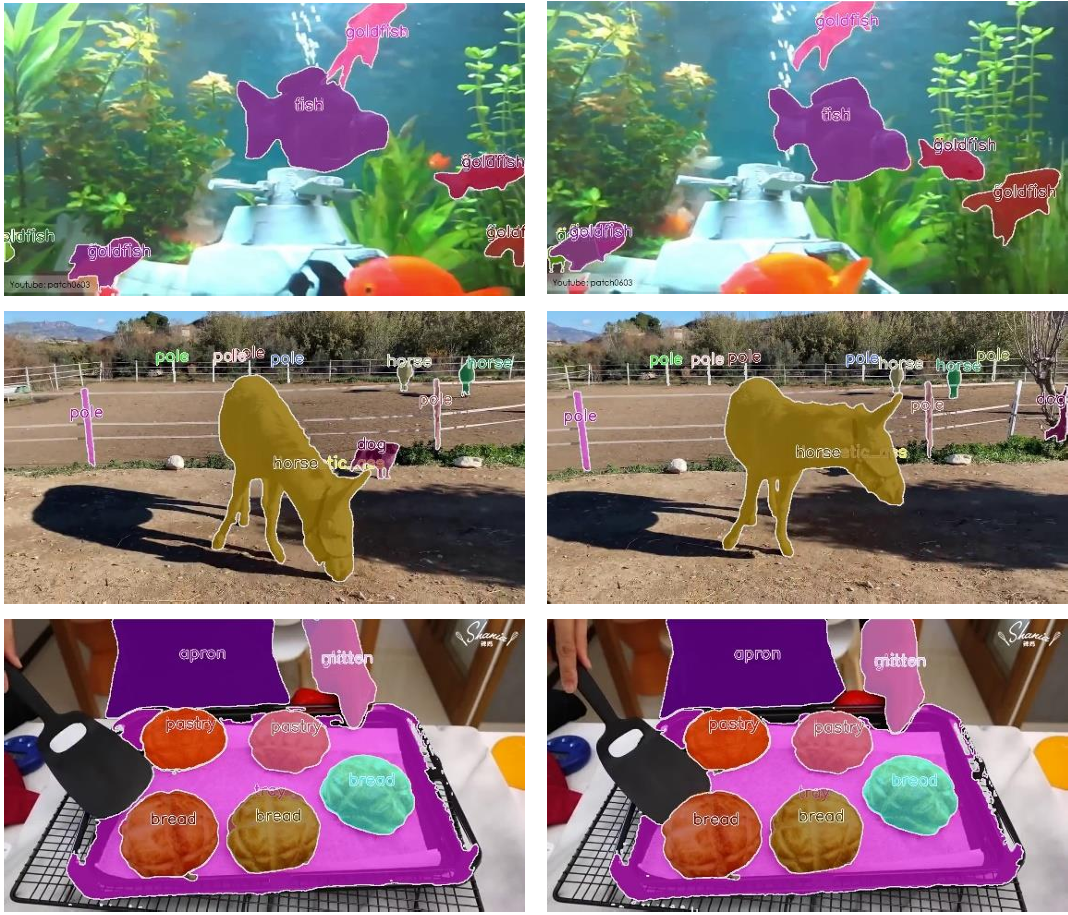
[9] Towards Real-Time Open-Vocabulary Video Instance SegmentationBin Yan, Martin Sundermeyer, David Joseph Tan, Huchuan Lu, Federico Tombari WACV, 2025 (Oral Presentation) arxiv / code / We address the challenge of performing open-vocabulary video instance segmentation (OV-VIS) in real-time. We propose TROY-VIS, which significantly improves processing speed while maintaining high accuracy. We introduce three key techniques: (1) Decoupled Attention Feature Enhancer (2) Flash Embedding Memory (3) Kernel Interpolation. |
|
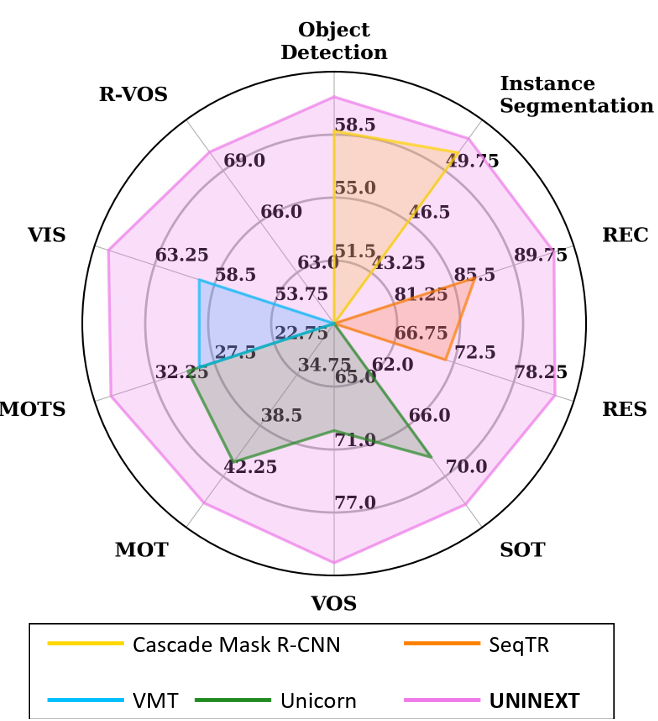
[8] Universal Instance Perception as Object Discovery and RetrievalBin Yan, Yi Jiang*, Jiannan Wu, Dong Wang*, Ping Luo, Zehuan Yuan, Huchuan Lu CVPR, 2023 arxiv / code / we present a universal instance perception model of the next generation, termed UNINEXT. UNINEXT reformulates diverse instance perception tasks into a unified object discovery and retrieval paradigm and can flexibly perceive different types of objects by simply changing the input prompts. UNINEXT shows superior performance on 20 challenging benchmarks from 10 instance-level tasks including classical image-level tasks, vision-and-language tasks, and six video-level object tracking tasks. |
|
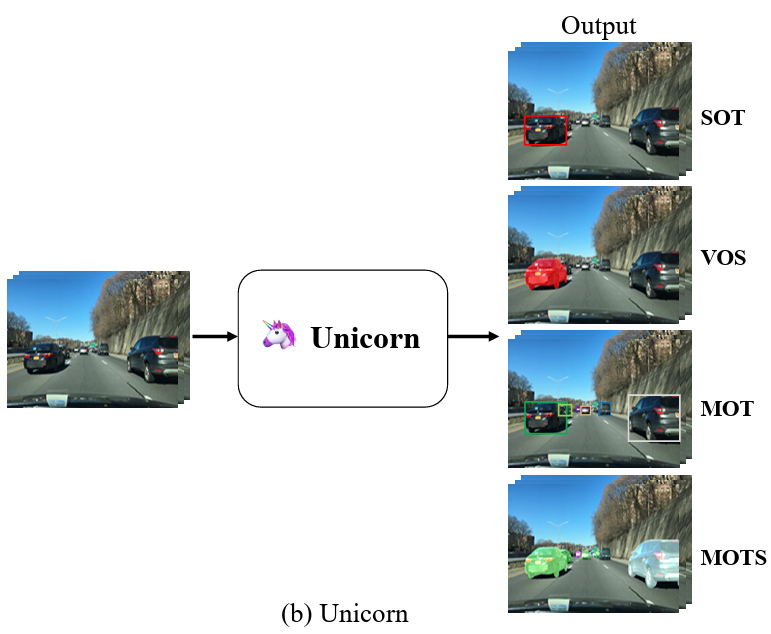
[7] Towards Grand Unification of Object TrackingBin Yan, Yi Jiang*, Peize Sun, Dong Wang*, Zehuan Yuan, Ping Luo, Huchuan Lu ECCV, 2022 (Oral Presentation) arxiv / code / We present a unified method, termed Unicorn, that can simultaneously solve four tracking problems (SOT, MOT, VOS, MOTS) with a single network using the same model parameters. Unicorn provides a unified solution, adopting the same input, backbone, embedding, and head across all tracking tasks. For the first time, we accomplish the great unification of the tracking network architecture and learning paradigm. Unicorn performs on-par or better than its task-specific counterparts in 8 tracking datasets. |
|
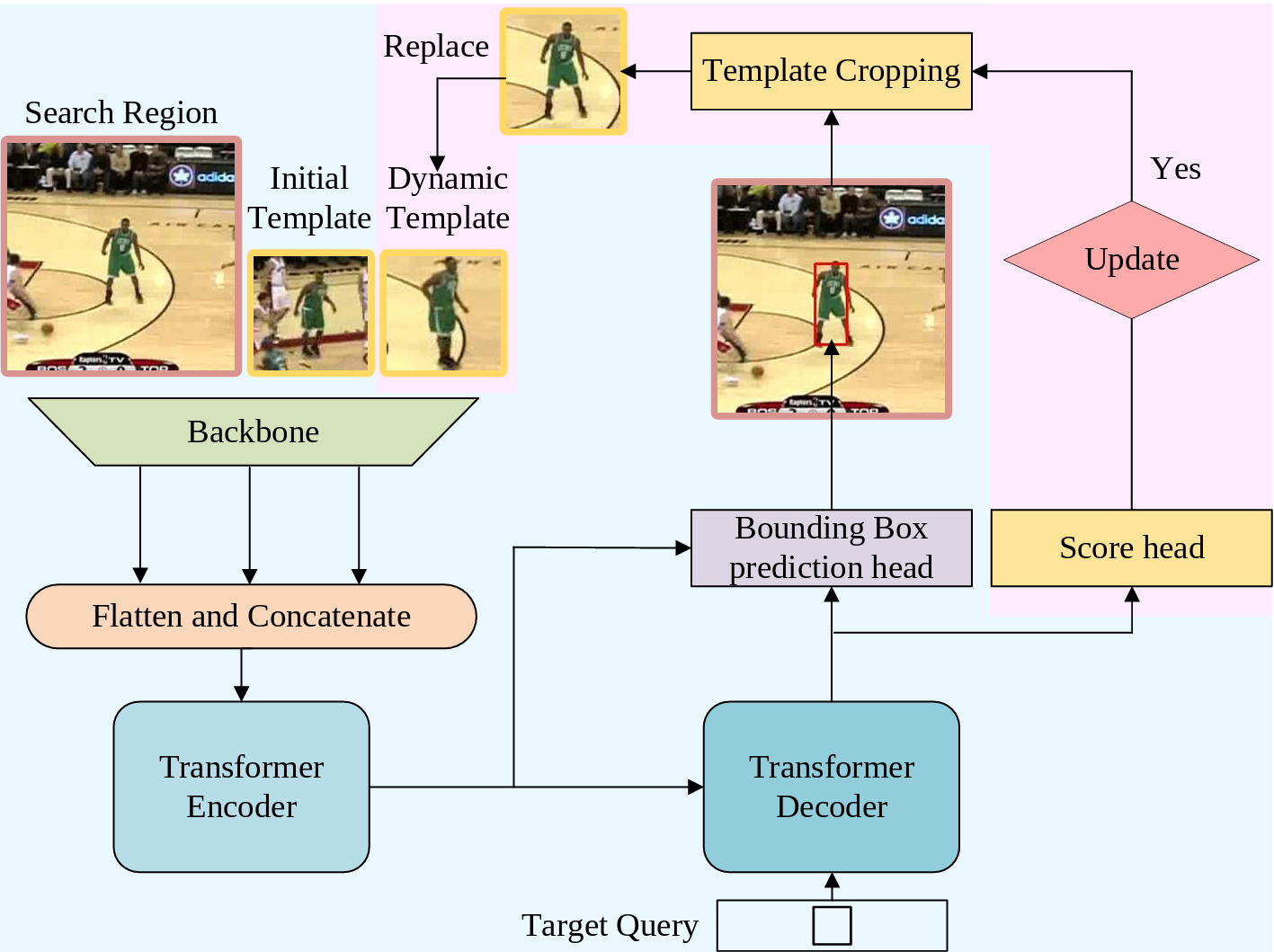
[6] Learning Spatio-Temporal Transformer for Visual TrackingBin Yan, Houwen Peng*, Jianlong Fu, Dong Wang*, Huchuan Lu ICCV, 2021 arxiv / code / We present a new tracking architecture with an encoder-decoder transformer as the key component. Our method casts object tracking as a direct bounding box prediction problem. The whole method is end-to-end, does not need any postprocessing steps, thus largely simplifying existing tracking pipelines. The proposed tracker achieves state-of-the-art performance on five challenging short-term and long-term benchmarks, while running at real-time speed, being 6x faster than Siam R-CNN. |
|
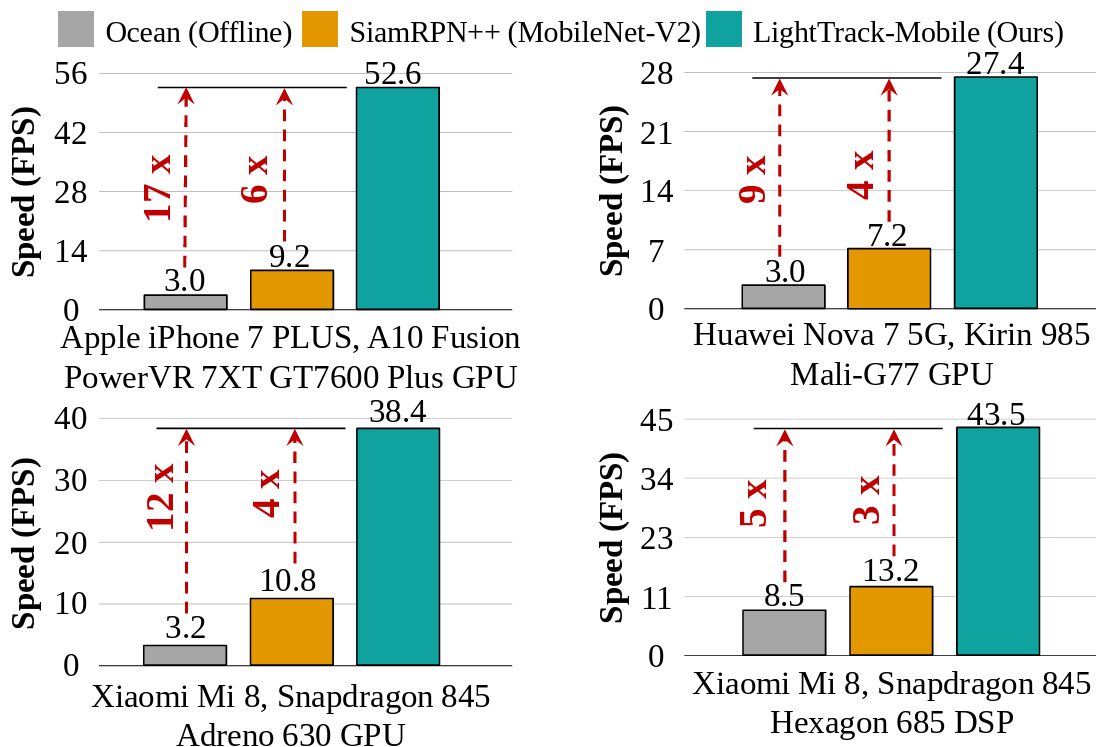
[5] LightTrack: Finding Lightweight Neural Networks for Object Tracking via One-Shot Architecture SearchBin Yan*, Houwen Peng*, Kan Wu*, Dong Wang, Jianlong Fu, Huchuan Lu CVPR, 2021 arxiv / code / We present LightTrack, which uses neural architecture search to design more lightweight and efficient object trackers. It can find trackers that achieve superior performance compared to handcrafted SOTA trackers, while using much fewer model Flops and parameters. On Snapdragon 845 Adreno GPU, LightTrack runs 12x faster than Ocean, while using 13x fewer parameters and 38x fewer Flops. |
|
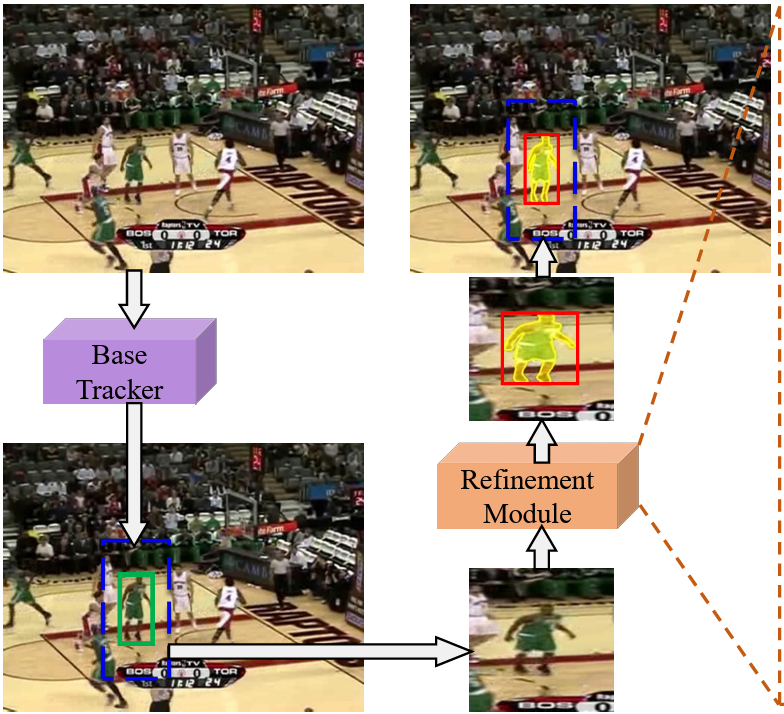
[4] Alpha-Refine: Boosting Tracking Performance by Precise Bounding Box EstimationBin Yan*, Xinyu Zhang*, Dong Wang, Huchuan Lu, Xiaoyun Yang CVPR, 2021 arxiv / code / We present Alpha-Refine, a flexible and accurate refinement module, which can significantly improve the base trackers’ box estimation quality. Alpha-Refine adopts a pixel-wise correlation, a corner prediction head, and an auxiliary mask head as the core components. Comprehensive experiments on diverse benchmarks with multiple base trackers show that our approach significantly improves the base tracker’s performance with little extra latency. |
|
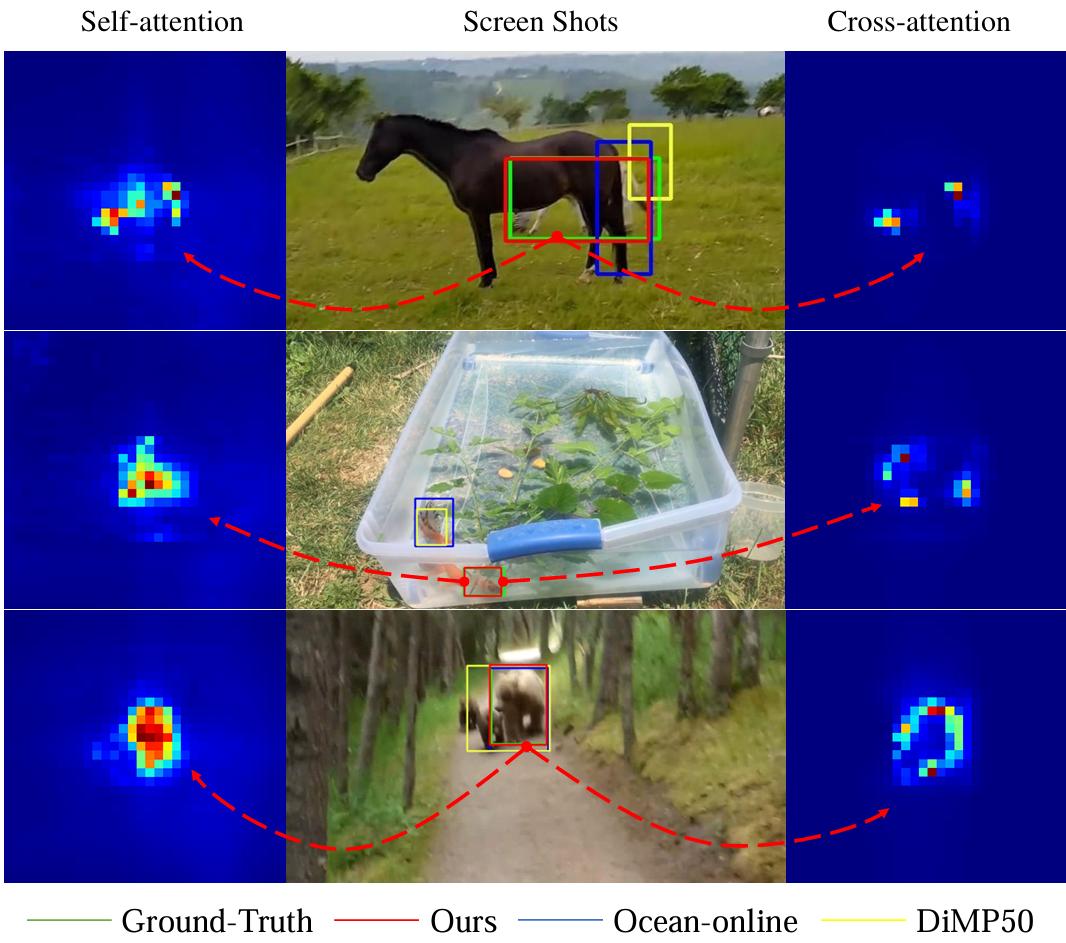
[3] Transformer TrackingXin Chen*, Bin Yan*, Jiawen Zhu, Dong Wang, Xiaoyun Yang, Huchuan Lu CVPR, 2021 arxiv / code / We present a Transformer tracking method named TransT, which effectively combines the template and search region features solely using attention. The proposed method includes an ego-context augment module based on self-attention and a cross-feature augment module based on cross-attention. TransT achieves very promising results on six challenging datasets. |
|
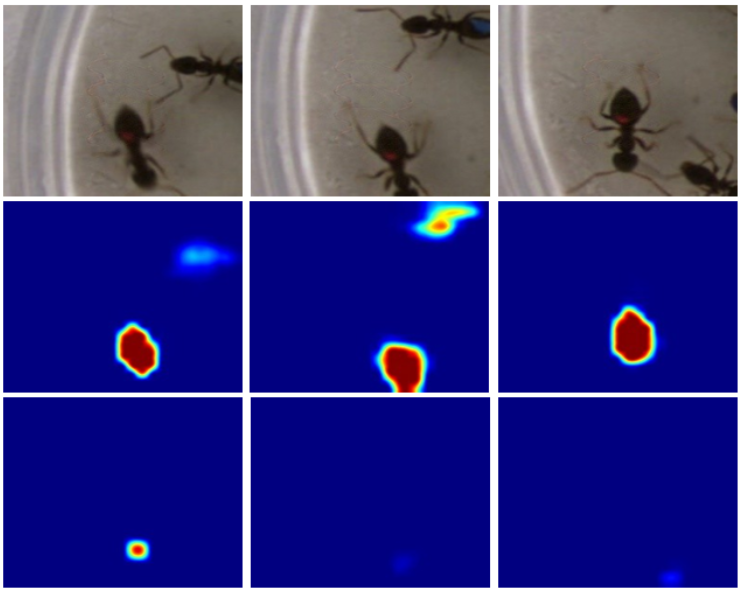
[2] Cooling-Shrinking Attack: Blinding the Tracker with Imperceptible NoisesBin Yan, Dong Wang, Huchuan Lu, Xiaoyun Yang CVPR, 2020 arxiv / code / We present the Cooling-Shrinking Attack (CSA) to deceive object trackers. An effective and efficient perturbation generator is trained with a carefully designed adversarial loss, which can simultaneously cool hot regions where the target exists on the heatmaps and force the predicted bounding box to shrink. Our method can effectively fool the trackers by adding small perturbations to the template or the search regions and has good transferability. |
|
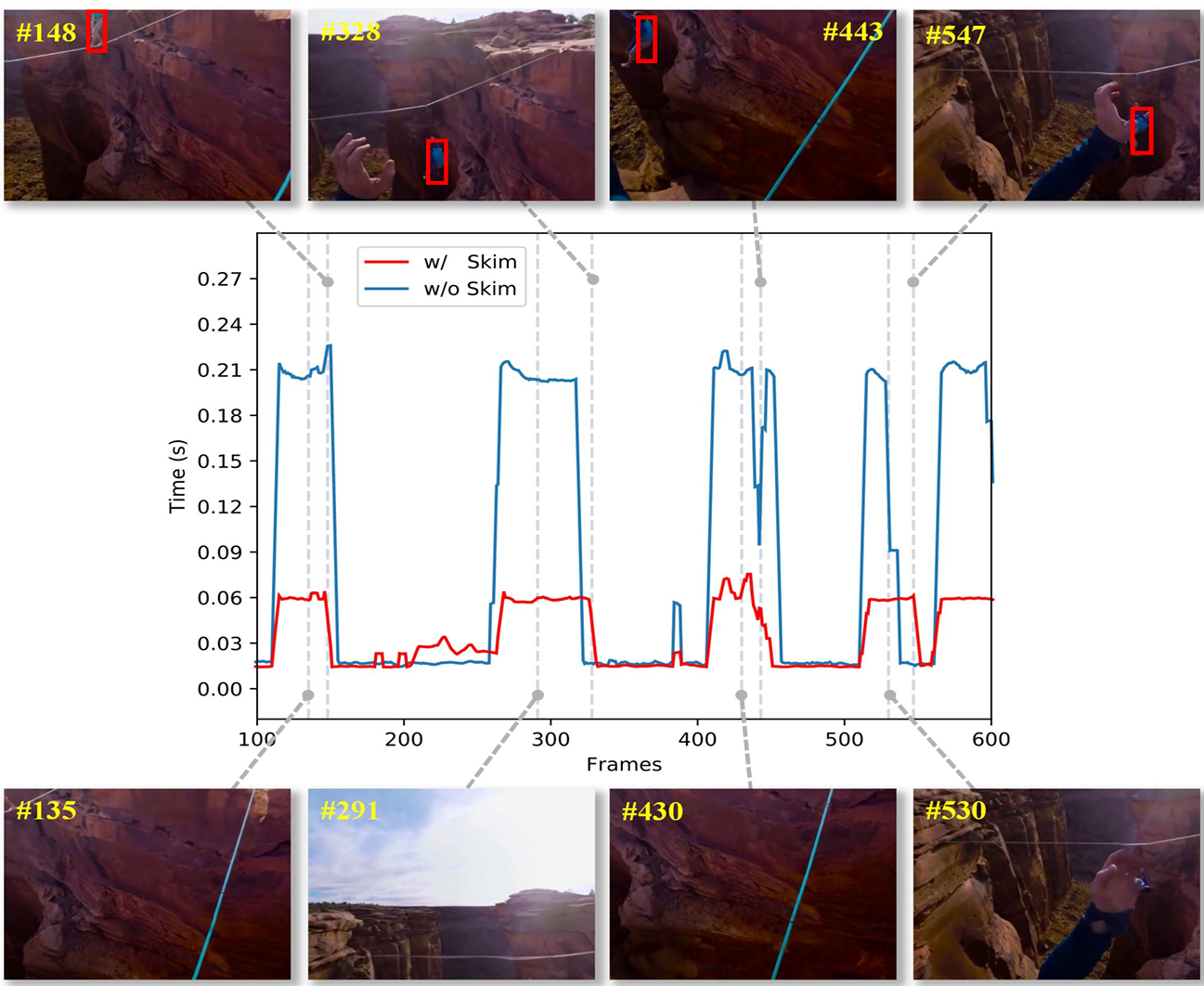
[1] ‘Skimming-Perusal’ Tracking: A Framework for Real-Time and Robust Long-term TrackingBin Yan*, Haojie Zhao*, Dong Wang, Huchuan Lu, Xiaoyun Yang ICCV, 2019 arxiv / code / We present SPLT, a robust and real-time long-term tracking framework based on the skimming and perusal modules. The perusal module consists of an effective bounding box regressor and a robust target verifier. Besides, a novel skimming module is designed to speed up the image-wide global search. The proposed method runs in real-time and achieves the best performance on the VOT-2018 long-term and OxUvA long-term benchmarks. |
|
Design and source code from Goutam Bhat's website. |